The Ultimate Trading Guide: 52. Swing Trading
Swing trading is a popular trading strategy that aims to capture gains in a stock or any financial instrument over a period of days to several weeks. Unlike day trading, which involves making multiple trades within a single day, or long-term investing, which can span several years, swing trading occupies a middle ground. This strategy leverages technical analysis, market sentiment, and fundamental factors to identify potential price movements. This chapter from "The Ultimate Trading Guide" by BellsForex will explore the intricacies of swing trading, its advantages, strategies for success, and a detailed case study illustrating its practical application.
Understanding Swing Trading
Definition and Goals
Swing trading involves holding positions for a short to medium term, typically from one day to several weeks, to profit from expected price swings. The primary goal is to capture a portion of the potential price movement. Swing traders use various technical analysis tools to identify entry and exit points, focusing on price trends, patterns, and momentum.
Key Characteristics
- Time Frame: Positions are held longer than day trades but shorter than long-term investments, usually ranging from a few days to a few weeks.
- Technical Analysis: Heavy reliance on charts, patterns, and technical indicators to make trading decisions.
- Flexibility: Swing trading can be applied to various financial instruments, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
- Risk Management: Emphasis on managing risk through stop-loss orders and position sizing to protect capital.
Advantages of Swing Trading
Potential for Higher Returns
Swing trading aims to capture significant price movements, which can lead to higher returns compared to longer-term strategies. By taking advantage of short to medium-term trends, traders can accumulate profits more quickly.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Swing trading requires less time and attention compared to day trading, making it suitable for individuals who cannot monitor the markets constantly. Traders can review their positions and make adjustments outside of regular trading hours.
Risk Management
Swing traders can manage risk effectively by using stop-loss orders and setting predefined risk-reward ratios. This disciplined approach helps minimize losses and protect profits.
Adaptability
Swing trading strategies can be adapted to different market conditions. Whether the market is trending, range-bound, or experiencing volatility, swing traders can adjust their tactics to capitalize on prevailing conditions.
Key Strategies for Swing Trading
Technical Analysis Tools
- Moving Averages: Used to identify trend direction and potential reversal points. Commonly used moving averages include the 50-day and 200-day moving averages.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It helps identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): A trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Key price levels where the asset tends to find support as it falls or resistance as it rises. Identifying these levels helps determine entry and exit points.
Chart Patterns
- Head and Shoulders: A reversal pattern that can signal a change in trend direction.
- Double Top/Bottom: Patterns that indicate potential reversal points.
- Flags and Pennants: Continuation patterns that suggest the prevailing trend will resume after a brief consolidation period.
Risk Management Techniques
- Stop-Loss Orders: Predetermined price levels at which a trade is automatically closed to prevent further losses.
- Position Sizing: Determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade based on risk tolerance.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Setting a favorable risk-reward ratio (e.g., 1:3) to ensure potential profits outweigh potential losses.
Case Study: Swing Trading in the Forex Market
James, an experienced forex trader, decided to apply swing trading strategies to capitalize on short to medium-term price movements in the EUR/USD currency pair. With a background in technical analysis and a disciplined approach to risk management, James aimed to capture gains by leveraging market trends and patterns.
Initial Analysis
James began by conducting a thorough analysis of the EUR/USD pair. He reviewed historical price data and identified key support and resistance levels. Using a combination of moving averages, RSI, and MACD indicators, James assessed the current trend and momentum of the pair.
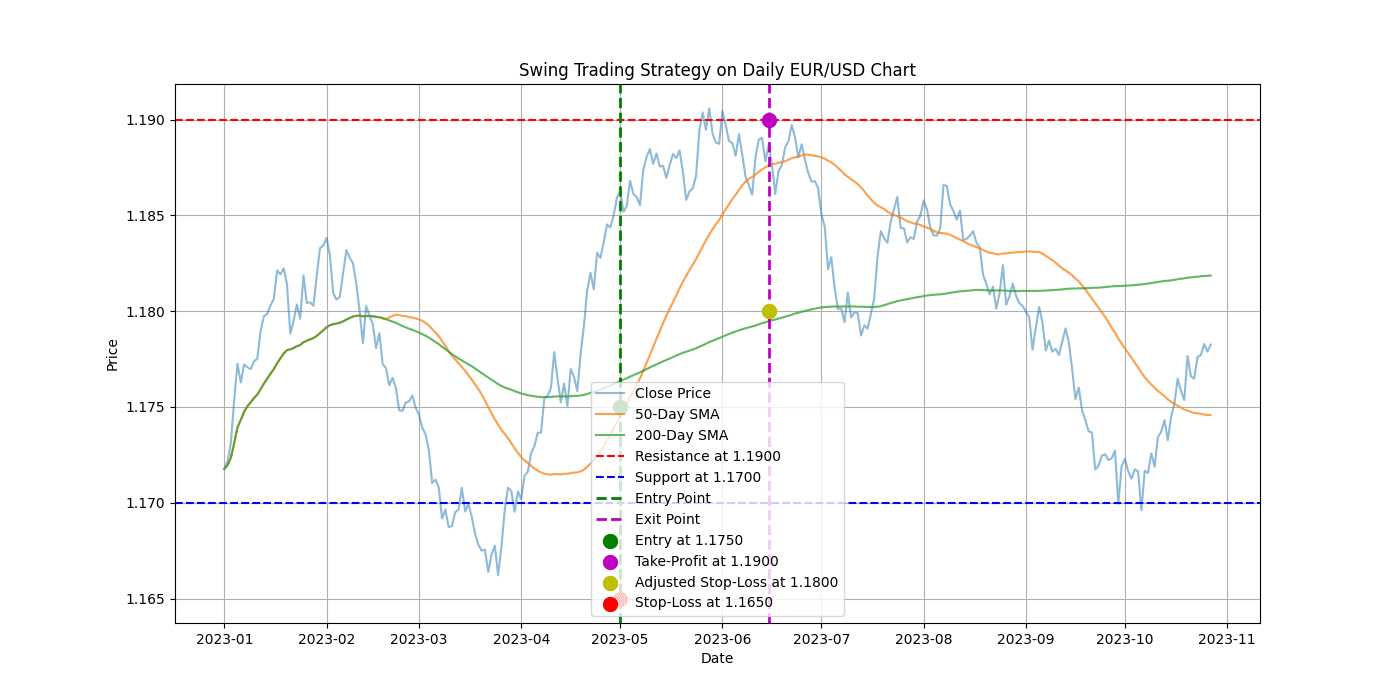
- Trend Identification: James noticed that the EUR/USD was in an uptrend, with the 50-day moving average crossing above the 200-day moving average (a bullish signal).
- Support and Resistance: He identified key resistance at 1.1900 and support at 1.1700.
- RSI and MACD: The RSI indicated that the pair was approaching overbought conditions, while the MACD showed bullish momentum.
Entry Point
James waited for a pullback to enter the trade at a more favorable price. When the EUR/USD retraced to the 1.1750 level (near the identified support), he initiated a long position, anticipating a continuation of the uptrend.
Risk Management
To manage risk, James set a stop-loss order at 1.1650, just below the support level. This stop-loss placement limited his potential loss to 100 pips. Additionally, he set a take-profit order at 1.1900, targeting the resistance level for a potential gain of 150 pips. This setup provided a risk-reward ratio of 1:1.5, aligning with James's trading plan.
Trade Execution and Monitoring
Over the next few days, James monitored the trade closely. He regularly reviewed technical indicators and market news to ensure his trade remained valid. The EUR/USD pair gradually moved higher, reflecting the continued bullish sentiment.
Adjustments and Outcome
As the price approached the 1.1900 resistance level, James noticed a weakening momentum indicated by a bearish divergence on the MACD. To protect his gains, he adjusted his stop-loss order to 1.1800, locking in a minimum profit of 50 pips.
Eventually, the EUR/USD reached the 1.1900 target, and James's take-profit order was triggered. He exited the trade with a profit of 150 pips, successfully capitalizing on the short to medium-term price movement.
Lessons Learned
- Patience and Discipline: James demonstrated patience by waiting for a favorable entry point and discipline by adhering to his risk management rules.
- Technical Analysis: Utilizing a combination of technical indicators and chart patterns helped James make informed trading decisions.
- Adjusting Strategies: By regularly reviewing his trade and making necessary adjustments, James effectively managed risk and protected his profits.
Final Remarks
Swing trading offers a compelling approach for traders looking to capitalize on short to medium-term price movements. By leveraging technical analysis, chart patterns, and disciplined risk management, traders can enhance their profitability and achieve consistent results. The case study of James's forex trade highlights the practical application of swing trading strategies and underscores the importance of patience, discipline, and continuous learning.
We believe that swing trading can be a valuable addition
to a trader's toolkit. Whether you're a novice or an experienced trader,
mastering swing trading requires a commitment to regular analysis, risk
management, and adaptability. By following the principles outlined in
this chapter of "The Ultimate Trading Guide," traders can navigate the
complexities of financial markets with greater confidence and achieve
their trading goals.




